의약식물 Luo Han Guo에 관한 연구
Siraitia grosvenorii (Swingle) C. Jef-frey ex Lu et Z. Y. Zhang is the dried fruit of a dioecious, dioecious perennial vine in the family Cucurbitaceae. It is cool in nature, sweet in taste, and enters the lung meridian. It has the effects of clearing away heat from the lungs, moistening the lungs, relieving sore throat and improving voice, and lubricating the intestines to promote bowel movement. It is used to treat cough due to lung heat, sore throat with loss of voice, and constipation due to dryness in the intestines [1]. As a precious medicinal and sweetening plant unique to China, Luo Han Guo is mainly produced in Yongfu, Lingui and Longsheng, etc., in Guangxi. The fruit of Luo Han Guo contains a variety of sweet glycosides, among which Mogroside V is one of the strongest non-sugar sweeteners in the world, about 300 times sweeter than sucrose. It is widely used in foods, health products and medicines, and is an ideal sugar substitute for diabetics, obese people and hypertensive patients [2]. This paper reviews the taxonomic status, geographical distribution, main cultivated varieties, breeding and cultivation techniques, chemical composition, pharmacological effects and molecular biology research of Luo Han Guo, with a view to providing a reference for further in-depth research, development and utilization of Luo Han Guo.

시래기 (Siraitia grosvenori)의 분류학적 현황 1
메릴 (Merrill)은 1934년 S. silomaradjae를 모식종으로 하는 새로운 속 (Siraitia)을 처음 만들었지만 인정받지 못했다.1941년, 미국 Swingle은 탄잉화 1호 표본 (광시 용푸현에서 수집)을 바탕으로 뤄한궈를 감별한 후 뤄한궈를 Cucurbitaceae 과에 속하는 모모디카속 (Momordica)의 종으로 분류했다.1979년, 영국의 식물학자 제프리 (Jeffrey)는이 표본을 연구한 후, Luo Han Guo 가 Momordica 속에 속하지 않고 Thladiantha 속에 속한다는 결론을 내렸고,이 식물의 건더기가 끝에서 두 갈래가 되고 두 갈래가 갈라진 지점에서 위아래로 비틀린 사실을 근거로 Luohan fruit이 Momordica 속에 속하지 않고 Thladiantha grosvenorii (Swingle) C. Jeffrey에 속한다고 믿었고,이 표본을 Thladiantha grosvenorii (Swingle) C. Jeffrey 라고 명명했다.이에 대해 중국의 많은 학자들은 회의적이다 [3].1997년 좡웨이젠 등 [4]은 최종적으로 뤄한궈의 염색체 수가 x = 14인 반면, Tribulus 속의 염색체 수는 x = 9, Momordica 속의 염색체 수는 x = 11 또는 14 임을 밝혀냈다.또한 루오한 구오의 꽃가루 형태는 트리불루스 테레스트리스와 상당히 다르며, 꽃가루 크기와 그물망 크기 [5]를 제외하면 모모르디카 차란티아, 트리불루스 테레스트리스와 더 유사하다.
1980년, 제프리 & 동안#39;s 표본을 조사하기 위해 중국을 방문한 중국과학원 식물학연구소 [6]의 루안민 등은 로한열매군의 수컷 anther locules 가 무형 또는 아형이고, 종자가 상당히 커 Momordica 속과는 분명히 다르다는 결론을 내렸다.그들은 또한이 식물들이 암꽃과 수꽃의 줄기에 분지가 없고, 수술은 3개가 아니라 5개이며, 열매 껍질은 매끄럽고 결절성 투사가 없기 때문에 Momordica 속에 들어갈 수 없다고 결론지었다.따라서, 시레이티아 (Siraitia)를 분리하고 새로운 속을 만들어야 한다는 제안이 있었다.그 후, 제프리는 Merrill이 제안한 속명 Siraitia를 그의 논문"East Asian Cucurbitaceae"에서 사용하고 모든 시레이티아 종을 시레이티아 속으로 옮겼다.현재 식물분류학에서는 일반적으로 1984년 제프리와 루안민 등의 분류학적 주장을 받아들여 [6], 장 (Siraitia grosvenorii, Swingle) C. 제프리 ex 루 et Z. Y. 장 (Siraitia grosvenorii, Swingle) C. 제프리 ex 루 et Z. Y. 장 (Siraitia grosvenorii, Swingle) C. 제프리 ex 루 et Z. Y. 장 (Siraitia grosvenorii, Zhang) 이며, 쿠쿠르비타과 (Cucurbitaceae)에 속하는 시레이티아속 (Siraitia)에 속하는 식물이다.그러나 초기 문헌에서 Siraitia grosvenorii는 여전히 때때로 Thladi-antha나 Momordica grosvenorii로 표기된다.
2. 시라이티아 그로스베노리 분포 (Distribution of Siraitia grosvenorii)
Siraitia grosvenorii 자원은 주로 중국의 광시, 광둥, 후난, 구이저우, 하이난, 장시성 (지역)의 일부 산간 지역에 분포되어 있다.이들 지역은 해발 250~1400m, 해발 106.5°-115.0 °, 북위 21.0°-24.5 °로 습윤한 열대 · 아열대 기후를 보인다. 하지만, 그것의 배포는 공평하지 않다.그 중 광시의 용푸현과 링기현은 뤄한궈 [7] 재배의 중심지이다.뤄한궈는 동쪽의 허저우시의 자오핑군, 남쪽의 친저우시의 푸베이군, 서쪽의 바이즈시의 링윈군, 북쪽의 구이린시의 링기군까지 광시에 널리 분포한다.그 중 진쑤야오족자치구의 다야오산이 가장 집중된 분포를 보인다 [8].
뤄화고의 주요 재배 품종 3가지
뤄화고의 주요 재배 품종은 칭피궈, 둥관궈, 라장궈, 창탄궈, 홍마오궈, 차산궈 등이 있다.바이러스성 질병, 뿌리매듭선충병, 세균시들음, 초파리 등으로 인한 위해가 심각하고 조직배양을 묘목 전파를 위해 사용하면 좋은 품종의 빠른 번식 및 정화의 목적을 달성할 수 있기 때문에 최근 볼린, 칭피 등 품종의 조직배양 묘목이 뤄한궈 생산지에서 널리 보급되고 있다.그 중 볼린 3호는 볼린 2호 녹색껍질 과일에서 성공적으로 선발된 Luo Han Guo의 새로운 균주이다.apical shoot 소독과 신속한 전파, 방향성 재배와 정화 및 회춘 후 2003년에 성공적으로 재배되었다.
It has excellent characteristics such as wide adaptability, well-developed roots, vigorous growth, drought and fertilizer tolerance, concentrated flowering, early fruiting and high yield, low pest and disease damage, few physiological fruit cracks, high rate of medium and large fruits, good quality, and stable seed characteristics [9]. Yongqing No. 1 is a female clonal variety that was produced by crossing a winter melon fruit as the male parent with a Longjiang green-skinned fruit as the female parent, followed by two years of single plant selection and tissue culture breeding. The fruits of this variety are long and oval, with a large fruit rate of up to 73.48% with an average single fruit weight of 100 g. The content of sweetener V, total fruit glycoside, total sugar, water extract and vitamin C is as high as 1.03%, 8.84%, 17.40%, 37.90% and 3.02 mg/g, respectively. It has good yield and strong stress resistance, with up to
헥타르당 16만 5 천 [10].
뤄hanguo의 전파 및 재배 기술 4
뤄한구오의 주요 전통 전파 기술은 종자 전파, 덩이줄기 전파, 겹치기 전파, 꺾꽂이 전파, 접목 전파 등이다.현재 바이러스성 질병, 뿌리매듭 선충병, 초파리 감염 등 생산지역의 심각한 사태와 더불어 환경을 희생하여 산림을 벌채하여 토양침식, 서식지 훼손 등을 초래하는 등 전통적인 재배방식이 한편으로는 전통적인 전파기술이 변화되고,그리고 조직 배양을 이용하여 바이러스가 없는 묘목을 얻는 실험 연구가 상당히 진척되었다 [11, 12].그중 광시약용식물원, 광시식물연구소, 길림하이테크구 베를린생물기술유한회사는 근년에 뤄화고의 우수한 균주 선발, 육종, 쾌속 번식을 진행하여 뤄화고의 스트레스 저항력을 일정한 정도로 향상시켰고 생산량 증가 및 품질 향상의 목표를 달성했다.현재 청피열매, 볼린 등 품종의 조직배양묘목이 생산지역에서 널리 보급되고 있으며;한편 뤄화고의 전통적인 언덕 재배법을 평지 재배법 [13]으로 바꾸려는 논의와 시도도 많이 있었다.
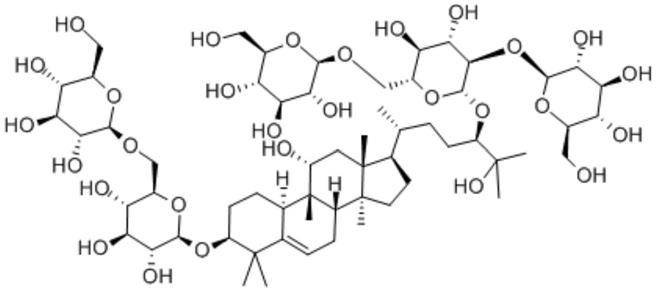
Luohanguo의 화학 성분 5
5.1 쿠쿠르비탄 트리테르페노이드 및 그 글리코사이드
At present, the main triterpenoid and its glycosides isolated and identified from the fruit of Luohanguo are: Simonoside I, Mogroside II E, Mogroside III, Mogroside III E, Mogroside IV, Mogroside V, 11-oxo-Mogroside V [14], Mogroside ⅣA and Mogroside ⅡA1 [15], Luohanguo digolyl benzoate [16], and Luohanguo neoglycoside [17]. The above components are the main sweet components of Luohanguo, accounting for 3.755% to 3.858% of the dried fruit content. Among them, Mogroside V is the main sweetening component, while Simonoside I is the sweetest component of the cucurbitane triterpene glycosides. When its content is 0.01%, the sweetness of the two is 256 to 344 times and 563 times that of a 5% sucrose aqueous solution, respectively. In addition, Luo Han Guo acid A and Luo Han Guo acid B [18] and Luo Han Guo acid E [19] have been isolated and identified from the root of Luo Han Guo.
단백질과 아미노산 5.2
쑤웨이쿤 등 [20]은 말린 뤄한궈 열매의 단백질 함량이 7.1%에서 7.8% 임을 발견했다.가수분해물에서는 검출되지 않은 트립토판을 제외하고 인체에 필요한 8개의 필수 아미노산을 포함하여 모두 18개의 아미노산이 존재한다.함량이 가장 높은 것은 글루타민산과 아스파라트산이며, Luo Han Guo는 특정 영양 가치가 있음을 보여줍니다.
5. 3 플 라보 노이 드
Si Jianyong et al. [21] isolated two flavonoid glycoside components from fresh Luo Han Guo aqueous extract: kaempferol-3,7-α-L-dirhamnoside and kaempferol-3-O-α-L-rhamnoside-7-O-[β-D-glucopyranosyl-(1-2)-O-L-rhamnoside]. Chen Quanbin et al. [22] isolated and identified kaempferol-3,7-O-α-L-dirhamnoside and quercetin-3-O-β-D-glucose-7-O-α-L-rhamnoside from the leaves of Luo Han Guo, with kaempferol and quercetin as the aglycones. Liao Riquan et al. [23] isolated and identified luohangol benzoate, bis[5-formylfurfuryl] ether, 5-hydroxymethyl furfuroic acid, succinic acid, magnolol, kaempferol, kaempferol-3,7-0-a-L-dirhamnoside, of which bis[5-formylfurfuryl] ether, 5-hydroxymethyl furfural and magnolol were isolated from Luo Han Guo for the first time.
5.4기타 성분
The fresh fruit of Luo Han Guo contains D-mannitol[24];잘 익은 과일에는 26가지 무기원소 (그 중 16가지는 인체에 필수) [25]와 다량의 포도당과 과당 [26]이 함유되어 있다;씨유는 불포화지방산 [27]이 풍부하다.
Luo Han Guo의 약리학적 효과 6
6.1 거담 및 기침 억제 효과
Luo Han Guo Mogroside V can increase the secretion of phenol red in the trachea of mice, promote the movement of mucus in the esophagus of frogs, and inhibit ammonia-induced coughing in mice. However, it has no significant effect on guinea pig asthma induced by citric acid, indicating that Luo Han Guo sweet glycosides have expectorant and antitussive effects [28].
6.2 항균효과
Su Huanqun et al. [29]은 그것을 혼탁성으로 발견했다Luo 한 Guo 추출물can significantly limit the growth and acid production ability of Streptococcus mutans, thereby inhibiting its cariogenic effect. The inhibition rates of the ethanol extract of the leaves and stems of Luo Han Guo (50.0 mg/mL) on Pseudomonas aeruginosa were 90.9% and 76.7%, respectively. In addition, the inhibition rate of the above stem extract on Escherichia coli was also as high as 70.2% [30].
6.3 면역기능
Luo Han Guo sweet glycoside는 정상 마우스의 면역 기능에 큰 영향을 미치지 않지만 대식세포의 식세포 기능과 cyclophosphamide (CTX) 면역 억제 마우스에서 T 세포의 증식 효과를 크게 향상시킬 수 있습니다 [31].Luo Han Guo 물 추출물은 정상 쥐의 체액 및 세포 면역 기능을 향상시키고 쥐의 비특이적 면역 기능을 향상시킬 수 있습니다 [29].
항암 효과 6.4
루오한궈 추출물을 쥐에 투여한 체외 실험 결과, 루오한궈 스위틴 V의 항암 효과는 스테비오사이드 [32]에 필적하거나 더 강한 것으로 밝혀졌다.
6.5 항산화 효과
Monk fruit extract can effectively remove free radicals, inhibit the oxidation and hemolysis of red blood cells, and the production of malondialdehyde (MDA), indicating that it has antioxidant activity, and monk fruit glycosides are the main antioxidant active ingredients [33].
몽크 열매에 대한 분자생물학 연구 7
좐한궈에 대한 초기 분자생물학 연구는 RFLP [34], RAPD [35-37], ISSR [38], AFLP [39], SRAP [40]과 같은 분자표지 기법을 이용한 연구로 제한되었으며, 이들은 좐한궈의 유전적 다양성, 친족관계, 성감별, 유전적 배경, 지문 및 유전자 지도를 연구하는데 사용되었다.일부 연구자들은 2세대 high-throughput Solexa sequencing 기술을 이용하여 뤄한구 열매의 전사체와 수분 후 발현 프로파일을 3 d, 50 d, 70 d로 하여 43,891개의 유니젠을 얻었으며, 그 중 739개는 Luohanguo 이차대사와 관련된 유니젠, 60개는 테르펜 골격 합성에 관련된 유니젠이었다.transcriptome 데이터를 이용하여, Luo Han Guo sweet glycoside V의 생합성 경로에 있는 모든 유전자들을 발견하였으며, 20개의 Luo Han Guo glycoside 골질 합성 유전자와 2 종류의 구조 변형 유전자 (cytochrome P450 유전자와 glycosyltransferase 유전자)를 포함하고 있다.또한 80개의 P450 유전자, 72개의 glycosyltransferase 유전자 및 90개의 glucosyltransferase 유전자를 얻었다.발현 프로파일 스크리닝과 함께 loganin V의 합성과 관련이 있을 수 있는 6개의 후보 UDPG 유전자를 얻었다.RACE 기술을 이용하여 16개의 골격 합성 유전자와 5'또는 3'단편을 갖는 2개의 유전자를 cloning 하였으며, 6개의 전장 CYP450 유전자와 7개의 전장 glucosyltransferase 유전자도 cloning 하였다.전사체 및 발현 프로파일의 해독은 Luo Han Guo의 기능 게놈과 감미료 V의 생합성의 분자 메커니즘에 대한 연구를 위한 견고한 토대를 마련합니다.
8 전망
중요한 약용 및 식용 식물 자원으로서 Luo Han Guo는 국내외에서 오랜 명성을 가진 중국에서 잘 알려진 특산품이자 전통적인 수출 상품입니다.그러나 바이러스성 질병, 뿌리매듭 선충 질병 및 초파리는 항상 뤄한궈 산업의 건강한 발전을 제한했다.따라서, 재배 환경, 식물, 과일의 오염의 농약 오염을 피하기 위해 화학 약제의 사용을 최소화하고 엄격하게 통제하기 위해 농업과 생물학적 제어에 초점을 맞춘 포괄적인 제어 방법을 구현해야합니다;이와 동시에 질병과 곤충에 강한 뤄한구오 품종을 사육하기 위해 노력해야 한다.

뤄화구는 재배 환경, 좁은 재배 면적, 재배 장벽 등에 대한 요구가 엄격하다.연속작물의 농작물은 해충과 질병에 극히 취약한데 해마다 재배면적을 변경하려면 많은 인력, 물자자원과 재력이 필요하다.또한 현재 생산지역은 여전히 전통적인 재배방식을 주로 사용하고 있어 산림을 벌채하는 경우가 많아 토양침식 및 서식지 악화 등 불리한 결과를 초래하고 있다.이러한 이유로, 필자는 가능한 한 빨리 Luo Han Guo의 지속적인 작물의 장애물을 극복하기 위해 재배지의 토양 미생물에 대한 연구를 강화해야한다고 생각합니다.
Luo Han Guo is a unisexual, dioecious plant. The pollen of male flowers is heavy and sticky, and has a bitter taste. Relying solely on wind or insects to spread pollen will not result in a high rate of fertilization. Only artificial pollination can ensure production, and pollination is the process that requires the most labor. In recent years, a method that is easier and more effective than pollination with a bamboo skewer has been developed in production practice: Press the male flower petals to the fruit stalk to expose the stamens, and lightly touch the side with dense pollen to the female stigma. Investigations have found that the same species of plant, the winged Luohanguo, is highly resistant, has large fruits, and a high yield, making it a good material for breeding. Moreover, individual plants have bisexual flowers that bear fruit without human intervention, which is an atavistic phenomenon that provides insight into the evolution of angiosperms. Further research is needed on the winged Luohanguo, which has bisexual flowers, in order to solve the problem of Luohanguo's는 수분을 위한 인간의 개입에 의존한다.
재배환경의 파괴로 뤄화고의 생식이 심각하게 악화되었고 뤄화고의 생식 혁신을 실시해야 한다.
다배체 육종 기술을 뤄화고의 신품종 연구 개발에 응용하는 것은 원래 품종의 결함을 극복하는 효과적인 방법이다.단당류는 과실의 과육과 껍질에만 존재하고, 종자는 단당류를 포함하지 않고 종자유를 다량 함유하고 있기 때문에 채취 및 정제의 난도와 생산 비용이 크게 증가하므로, 기존 품종보다 단당류의 함량이 높고 과일 전체의 이용률이 높은 씨 없는 뤄화궈를 육성하는 것은 뤄화궈산업 전체의 발전을 위한 이정표이다.
참조:
[1] National Pharmacopoeia Commission of the People&의 약자#39;s 중화민국.약전 (Pharmacopoeia of the People's 중화민국 (Part I) [M].북경:중국의학과학기술출판사, 2010.197.
[2] Li Dianpeng, Zhang Hourui.광시 [廣西]의 특산식물 Luo Han Guo의 연구 및 응용.광시식물학, 2000, 20(3):270-276.
[3] 이장경, 우쟁이, 루안민.아과 Cucurbitales에 속하는 식물의 세포학적 관찰 (J.Yunnan Botanical Research, 1993, 15(1):101-104.
[4] 좡위젠, 린즈량, 정셴쿤.Luo Han Guo [J]의 염색체 유형에 대한 연구.한국열대 · 아열대식물학회지 1997, 5(2):23-25.
[5] 성우는 故 우키리.Luo Han Guo, Mu Baizi, Ku Gua, Henan Chi Jing Ying [J] 등 4가지 식물의 꽃가루 관찰 (Observation of pollen from four plants:Luo Han Guo, Mu Baizi, Ku Gua, and Henan Chi Jing Ying)광시식물학, 1981, 1(3):24-28.
[6] 루안민, 장지윤.중국 뤄hanguo 식물 [J].광시식물학, 1984, 4(1):27-33.
[7] 저량채, 장비유, 진량 등이 있다.Luohanguo 품종 및 자원의 조사 및 이용 [J.광시식물학, 1981, 1(3):29-33.
[8] 종시경.Luo Han Guo [J]의 연구 현황.광시 농학, 1992(4):164-166.
[9] 허진왕, 진장웨이, 리볼린.Luo Han Guo"Bolin No. 3"[J]의 새로운 균주의 고생산량 재배 기술.광시농업학회지, 2007, 22(1):46-47, 62.
[10] 마샤오준, 모창밍, 바이룽화 등.용칭 1호 [J] Luo Han Guo의 새로운 품종.한국원예학회지, 2008, 35(12):1855.
[11] 이풍, 장한명, 장신능 등.Luohanguo 조직배양묘의 재배에 관한 연구.광시식물학, 1990, 10(4):359-363.
[12] 푸창량, 마샤오준, 바이룽화 등.Luohanguo 바이러스 없는 묘목의 신속한 전파에 관한 연구 (J.한방의학, 2005, 36(8):1225-1229.
[13] 주바오민.연구논문:평원지역의 시레이티아 그로스베노리 (Siraitia grosvenorii) 재배기술에 관한 고찰 (硏究)광시원예학, 2004, 15(3):13-14.
[14] 마츠모토 K, 카사이 R, 오타니 K 등.Minor cucurbitane glycosides from fruits of Siraitia grosvenorii (Cucur-bitaceae) [J.Chem Pharm Bull, 1990, 38(7):2030-2032.
[15] 양서웨이, 장자녜, 취안중명.Siraitia grosvenorii [J]의 새로운 천연 사포닌.한약재, 2008, 39(6):810-814.
[16] 왕야핑, 천자누.시레이티아 그로venorii의 화학성분에 관한 연구 (Research on the chemical components of Siraitia grosvenorii [J.한약학, 1992, 23(2):61.
[17] 시자옹, 천디화, 장기 외.부제:Isolation and structural identification of triterpenoid glycosides in Luo Han Guo [J].「 Acta Botanica Sinica 」, 1996, 38(6):489-494.
[18] 왕슈펜, 루웬지, 천자위안 등.Luo Han Guo root (I) [J]의 화학성분에 관한 연구.한약재, 1996, 27 (9):515-518.
[19] 시자옹, 첸디화, 셴량 외.광시 (廣西) 특산식물인 Luo Han Guo root의 화학성분에 관한 연구 (硏究)대한약학회지 1999, 34 (12):918-920.
[20] 쑤웨이쿤, 멍리산.Luo Han Guo [J]의 단백질 함량 측정.Guangxi Plants, 1986, 6(3):295-296.
[21] 시자옹, 천디화, 장기 외.신선 Luo Han Guo의 flavonoid glycosides의 분리 및 구조 결정 (Isolation and structural determination of flavonoid glycosides in fresh Luo Han Guo)한국약학학회지 1994, 29(2):158-160.
[22] Chen Quanbin, Yang Jianxiang, Cheng Zhongquan 외.Luo Han Guo (Siraitia grosvenorii) [J]의 flavonoid glycosides의 분리 및 구조 식별 (Separation and structural identification of flavonoid glycosides from Luo Han Guo (Siraitia grosvenorii))광시과학, 2006, 13(1):35-36, 42.
[23] 랴오 리캉, 이준, 황시산 등.Luo Han Guo [J]의 화학조성에 관한 연구.「 Acta Botanica Boreali-Occidentalia Sinica 」, 2008, 28(6):1250-1254.
[24] 쑤웨이쿤, 멍리산, 리중야오.부제:Separation and identification of mannitol in Luo Han Guo [J].Guangxi Plants, 1990, 10(3):254-255.
[25] 멍시린, 저우치, 룽샤오이 외.Luo Han Guo의 무기 원소의 결정 및 분석과 그 뿌리 [J.Guangxi Traditional Chinese Medicine, 1989, 12(6):42.
[26] 쑤웨이쿤, 멍리산.Luo Han Guo의 영양성분 결정 (Determination of nutritional components of Luo Han Guo)Guangxi Plants, 1981, 1(2):50-51.
[27] 청주잉, 루오 실리안, 판 유파 외.광시식물의 유분에 대한 연구:50 종 식물 종자의 유분 조성 (I.광시식물 (Guangxi Plants), 1980(2):26-33.
[28] 왕팅, 황지홍, 장예민 등.몽크과일단 glycosides의 생물학적 활성에 관한 연구 (Research on the biological activity of monk fruit sweet glycosides [J.한약학, 1999, 30 (13):914-916.
[29] Su Huanqun, Chen Zaiyi.Luo Han Guo [J]에 대한 약리학 및 응용 연구.한의학, 2003, 26(10):771-772.
[30] 예민, 저잉.Luo Han Guo 잎과 줄기의 에탄올 추출물의 세균성 효과 (J.한국산농생물학회지, 2008, 27(1):42-46.
[31] 왕 Q, 왕 C, 다이 S 등.Luo Han Guo sweet saponin의 마우스 세포 면역기능에 대한 조절효과 (J.한국한의학, 2001, 24(11):811-812.
[32] Luo Han Guo [J]에서 단 물질의 항암 효과 Kijima T.외국의학:한의학 보문, 2003, 25(3):174.
[33] 장리친, 치샹양, 천웨이준 등.Luo Han Guo 추출물의 항산화 활성에 관한 연구.식품과학, 2006, 27(1):213-216.
[34] 위룽창, 이펑, 황시양 외.polyploid Luohanguo를 위한 PCR-RFLP 파라미터의 최적화 및 응용 [J].광시식물학, 2009, 29(6):889-893.
[35] 저우쥔야, 탕샤오칭.재배된 Luohanguo의 유전적 다양성의 RAPD 분석 (J.Molecular Plant Breeding, 2006, 4(1):71-78.
[36] 황장, 장휘핑, 천팅수 외.Luo Han Guo (J)의 생식질에 따른 유전적 관계에 대한 RAPD 분석.Fujian Fruit Tree, 2006(1):15-17.
[37] 위설링, 황지메이, 양화 외.Luo Han Guo [J]의 성 관련 RAPD 마커의 Clone 및 서열분석.후베이 농업과학, 2008, 47(3):251-253.
[38] 위룽창, 리홍, 장강 등.씨없는 Luo Han Guo와 그 부모의 유전적 배경에 대한 ISSR 분석 [J.한국원예과학회지, 2012, 39 (2):387-394.
[39] 태리, 왕유진, 유민 외.AFLP는 Siraitia grosvenorii의 DNA 지문 지도를 작성하고 묘목의 성별을 식별하는데 사용된다 [J].무한식물학연구, 2005, 23 (1):77-80.
[40] 류 L H, 마 X J, 웨이 J H 등.ISSR과 SRAP 마커를 기반으로 한 Luohanguo (Siraitia grosvenorii)의 첫 번째 유전자 연결 지도 [J.게놈 (Genome), 2011, 54(1):19-25.


 영어
영어 프랑스
프랑스 스페인
스페인 러시아
러시아 한국
한국 일본
일본




