희귀 Ginsenoside Rg1 Rb1에 관한 연구
인삼 (파낙 스인삼 C다. A. Meyer) is a perennial herb 에서이family Araliaceae 그리고is a traditional precious Chinese medicine. Ginsenosidesare one 의이ma에서active ingredients 의ginseng. They belong to the group 의triterpenoid glycosides 그리고are formed 에 의해the condensati에의a sugar 그리고a glycoside precursor. Studies have shown that ginsenosideshave a variety 의pharmacological effects [1-3]. After oral administration, most protopanaxadiol-type ginsenosidesare hydrolyzed by intestinal flora to ginsenosideC-K, Rg3, Rh2and PPD[4-5], and protopanaxatriol-type ginsenosides are mainly degraded to ginsenoside F1 and 20(S)-PPT[6- 7]. The metabolite C-K 의protopanaxadiol-type ginsenosides has significant antitumor activity in vitro and in vivo, and 의activity is enhanced compared to the precursor[8]. Rg1, Re and 20(S)-PPT have a strong anti-tumor 셀metastasis effect after oral administration, while only 20(S)-PPT has an anti-tumor effect when administered intravenously, indicating that the anti-tumor metastasis effect of Rg1 and Re after oral administrati에is produced by their metabolite 20(S)-PPT [9].
많은 연구에 따르면 장내 세균에 의해 진세노사이드 (ginsenoside) 가 탈글루코실화 (deglucosylation) 되어 두 개 또는 하나의 글리코시드 결합을 가진 희귀한 진세노사이드 (ginsenoside) 가 생성되며,이 진세노사이드 (ginsenoside)는 생물학적 활성이 더 강하다 [10].

생체 변환은 진세노사이드의 화학 구조를 변화시키고, 진세노사이드의 생체 내 이용률을 효과적으로 향상시키며, 약물의 임상 효능을 최적화하고, 부작용 [11]을 줄일 수 있다.진세노사이드의 생물학적 형질전환은 당화, 하이드록실화, 이중결합의 변화를 포함한다.ginsenosides의 당화는 주로 C-3, C-6 및 C-21에서 발생하며, glycoside 가수분해 및 당화 (glycosylation;일부 변환은 또한 C-3, C-12 및 C-17 사이드 사슬에서 일어나 메틸기와 히드록시기를 연결하고;이중 결합의 변형은 주로 C-24/C-25 이중 결합의 첨가 또는 산화를 포함한다.이 글은 최근 희귀진세노사이드 (ginsenoside)의 미생물 생물형질전환 개발, 모핵의 구조변화 및 유도체 응용에 대한 고찰을 통해 진세노사이드 및 유도체의 구조연구 및 응용에 이론적 기반을 제공하고자 한다.
희귀 진세노사이드의 구조 및 응용 1
희귀한 진세노사이드의 구조 1.1
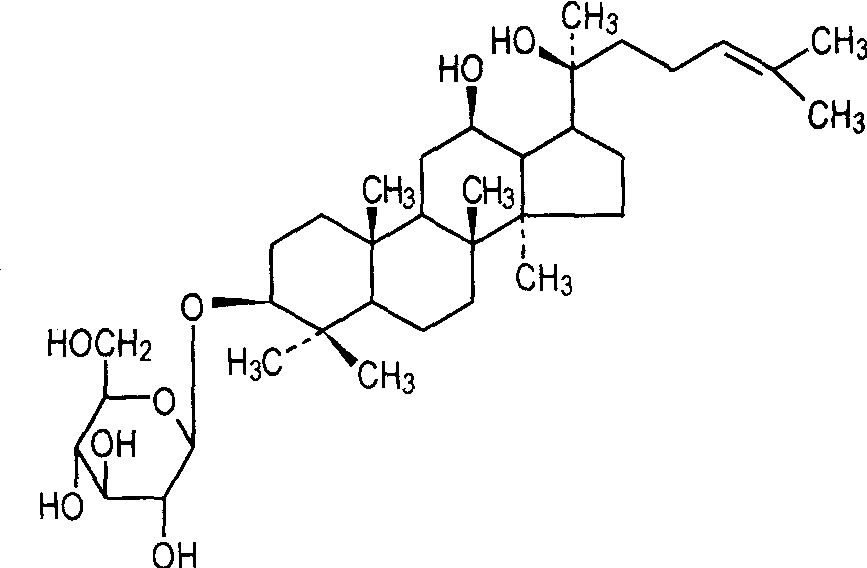
진세노사이드는 아글리콘의 구조에 따라 테트라사이클릭 트리테르페노이드와 펜타사이클릭 트리테르페노이드로 나뉜다.Protopanaxadiol-type ginsenosides (그림 1a) 및 protopanaxatriol-type ginsenosides (그림 1b)는 모두 dammarane-type tetracyclic triterpenoid ginsenosides, Oxytirone type saponins (그림 1c)는 furan ring을 포함하는 side chain을 갖는 tetracyclic triterpene saponin;oleanolic acid를 모핵으로 하는 oleanane 형 사포닌은 pentacyclic triterpene saponins에 속한다 (그림 1).
"희귀 진세노사이드"라는 이름은 자연적으로 낮은 양이나 거의 존재하지 않는 양에서 유래되었다.희귀한 진세노사이드는 주로 다마스카형 사포닌으로, 아글리콘의 C-3, C-6 및 C-20위치에 3개 이상의 설탕 모이어티가 부착되지 않고, 하나의 위치에 2개 이상의 설탕 모이어티가 부착되지 않는다.희귀한 진세노사이드는 주로 진세노사이드의 탈당이나 탈수에 의해 얻어진다.현재 확인된 주요 희귀 진세노사이드는 표 1과 같이 Rg3, Rg1, Rh1, Rh2, Rh3, RT3, F1, F2, C-K, PPD,PPT 등이다.
1.2 진귀한 인삼 사포닌 적용
희귀 한ginseng saponins are mainly found in red ginseng and black ginseng, and are the basis of the physiological activity of red ginseng and black ginseng, which is different 에서that of ginseng. 인삼 가루 and ginseng tablets sold on the marketonly grind the raw materials (ginseng, American ginseng, etc.) from which ginseng saponins are extracted 로powder, or add excipients and then press into tablets. Ginseng saponin tablets and capsules only extract the total ginsenosides from the medicinal herb, without further separation or transformation. This directly extracted ginsenoside needs to be broken down by specific enzymes before it can be absorbed by the body. However, these enzymes are either rare or absent in the human body. This results in low bioavailability and weak pharmacological effects in the human body.
현재 중국의 희귀 진세노사이드 제제 대부분은 단량체 성분인 Rh2 또는 Rg3를 포함하고 있다.진세노사이드 단량체 중 한 종류만을 포함하는 제조물을 하기 표 2에 나타내었다.
Common rare ginsenosides such as ginsenoside C-K, Rg3 and Rh2 have been used in clinical applications to improve the body'의 면역 건강 또는 보조 치료를 위해 다른 약물과 병용.한편, 희귀 진세노사이드 응용 연구는 여전히 진세노사이드 개발의 중요한 부분이다.본 연구진은 20(R)-ginsenoside를 원료로 사용하여 C-3위치와 tert-butoxycarbonyl glycine 사이의 에스테르화 반응을 통해 새로운 ginsenoside glycinate 유도체를 합성하였다.그리고이 유도체의 항암활성이 20(R)-ginsenoside (ic50>30 mmol/L)의 100배 이상임을 확인하였다.A11의 생체내 저해효과는 20(R)-ginsenoside (P<0.01)보다 유의적으로 나타났다.동시에 A11 투여 의존적으로 HeLa 세포의 증식, 이동 및 침입을 억제하고 apoptosis를 촉진한다 [12].진세노사이드 Rg4는 인삼 잎과 흑삼에서 발견되는 희귀한 진세노사이드다.Rg4는 염증을 억제하고 clp로 인한 패혈증에 대한 보호 효과를 나타낸다 [13].Rg5 형태와 안정적인 복잡 한 인간 purinergic 수용체를 12 (P2RY12) allosteric 상호작용을 통해, 잔류를 통해 활동 E188를 줄이고 R265, interleukin의 석방을 감소를 초래 한 (일) 6에서, IL-1 β와 종양 괴 요인-α에 혈장, 정맥의 염증 반응 형성을 억제하는 동안 개선 thrombi [14].진세노사이드 Rk1은 항종양 [15]을 가지고 있고 [16~17] 혈당을 조절하며 [18~19] 신경계를 보호하며, 진세노사이드 Rk5와 함께 사용할 경우 알칼리성 포스파타제 활성을 증가시킴으로써 골세포 분화와 성장을 촉진하여 [20] 골다공증을 치료한다.연구가 진행됨에 따라 희귀 진세노사이드와 그 유도체의 생물학적 활성이 더 많이 발견될 것이다.

희귀 진세노사이드의 생물형질전환 연구 현황 2
진세노사이드 형질전환의 주요 방법은 화학적 형질전환 (chemical transformation)과 생물학적 형질전환 (biotransformation)이다.화학적변환은 주로 글리코시드결합의 산-염기 가수분해, 산화적첨가, 아세틸화 등 반응을 리용하여 치환기를 변화시킨다.생물형질전환 (Biotransformation)은 미생물 세포를 이용하여 외인성 기질의 구조를 변형시키고, 신진대사 중에 생성되는 하나 이상의 효소를 이용하여 기질의 특정 부분 (군)에 대한 반응을 촉매함으로써 [21] 활성 성분의 함량과 약효를 증가시킨다.생물전환 방법에는 세균의 형질전환, 장내 동식물의 형질전환, 진균의 형질전환, 체외 효소촉매 등이 있으며, 급격한 반응조건, 환경오염, 부산물의 생성 등 화학적 형질전환 방법의 단점을 보완한다.그들은 연구 및 생산에 널리 사용된다.생물형질전환의 주요 반응 유형으로는 글리코사이드 가수분해 반응과 산화 환원 반응 [22]이 있으며, 그 중 글리코사이드 가수분해 반응이 가장 널리 사용된다 [23].최근에는 C-24 및 C-25위치에서의 첨가 반응도 점차 실제 생산에 응용되고 있다.
2.1 희귀 인삼 사포닌의 Glycoside 가수분해
인삼사포닌의 미생물 glycoside 가수분해 2.1.1
The metabolic pathway of ginseng saponins in vivo is an 중요 한part of the research on the structure-activity relationship of ginseng saponins. Stepwise deglycosylation is the main metabolic pathway of ginseng saponins in vivo. The rare ginseng saponins and aglycones produced by metabolism have significant pharmacological effects in the body. The main transformation products of ginsenoside Rd were found to be F2, Rg3, C-K, Rh2 and PPD; the main transformation products of ginsenoside F2 were C-K and PPD; the main transformation products of ginsenoside Rg3 are Rh2 and PPD[24]; and C-K and Rh2 can be converted to PPD[25]. Through the analysis of the transformation products of protopanaxatriol-type saponins Re, Rg1, Rh1, Rf, F1 and R1 in the human intestinal flora, their metabolites and transformation pathways were determined i.e., the conversion pathway of ginsenoside Re is Re →Rg1/Rg2 →Rh1/F1 →PPT; the conversion pathway of ginsenoside Rg1 is Rg1 →Rh1/F1 →PPT; the conversion pathway of ginsenoside Rf is Rf→Rh1 →PPT; and the metabolic pathway of notoginsenoside R1 is R1 →Rg1/Rg2 →Rh 1 →PPT[26].
in vitro에서 장내 세균에 의한 ginsenoside Rb1의 대사 경로는 탈글루코실화 과정이며, 장내 세균에 의한 ginsenoside Rb1의 가수분해 또한 단계적 탈글루코실화 과정이다 [27].생체 내 장내 세균에 의한 진세노사이드 대사도 마찬가지다.GUO 등 (28)은 광범위 항생제를 이용하여 무균쥐 모델을 만들고 쥐에서 장내 미생물군에 의한 노토삼 사포닌 (1.535 g/kg)의 전환을 확인하였다.그 결과 무균쥐의 혈장에서는 ginsenoside F1, Rh2, C-K, PPT 4가지 대사산물이 검출되었으나, 무균쥐의 혈장에서는 검출되지 않았다.따라서 체내 ginsenoside 대사의 기본법칙은 tetraglycoside → trisaccharide → disaccharide → monosaccharide → aglycone인 것으로 추론된다.
미생물에 존재하는 효소에는 많은 종류가 있는데, 효소는 당질을 전환시킬 수 있는 잠재력을 가지고 있다 [29].동시에 발효 후 제거된 당은 곰팡이의 생장과 번식을 위한 탄소원으로 사용될 수 있으며, 이를 통해 대사 작용을 통해 더 많은 효소를 생산할 수 있다 [30].따라서 여러 가지 미생물을 생물촉매로 사용하여 천연물의 생물변환에 중요한 역할을 할 수 있다.국내외 학자들은 박테리아와 균류를 이용하여 진세노사이드에 대한 생물형질전환 연구를 수행해 왔다 (그림 2).
연구결과 Aspergillus niger, Fusarium sp., Penicillium sp., Cordyceps sinensis 및 Armillaria mellea, Bifidobacterium breve, Bacillus sp., Lactococcus lactis 및 Lactobacillus plantarum sub sp., Terrabacter sp., Cellulosimicrobium cellulans sp.,및 Thermotoga thermarum은 진세노사이드 (ginsenoside) C-3 또는 C-20의 당 그룹을 대사시켜 희귀한 진세노사이드 (ginsenoside) 또는 아글리콘 (aglycones)을 생성할 수 있다 (표 3). Aspergillus niger는 진세노사이드 Rb1및 Rb3를 각각 진세노사이드 Rd, F2 및 C-K로 대사시킬 수 있다 [31, 38];또한 ginsenosides Rb2와 Rc의 3-O-Glc를 먼저 가수분해하고, 20-O-Ara를 가수분해하여 하나의 가수분해 경로를 만들 수 있다:Rb2 → C-O → C-Y → C-K, Rc → C-Mc1 → C-Mc → C-K, 그리고 주로 Rb3 → C-Mx1 → C-Mx → C-K의 경로를 통해 Rb3 20-O-Xly를 가수분해하고, Rb3 → Rd → F2 → CK [38] 경로를 통해 Rb3 20-O-Xly를 천천히 가수분해한다.Penicillium은 Rb1 → Rd → F2 → C-K 경로를 통해 진세노사이드 및 진세노사이드 단량체를 가수분해하여 희귀한 진세노사이드 (ginsenoside)를 생성한다 [32-33,52];푸세륨은 발효배양을 통해 진세노사이드 총 사포닌을 희귀 진세노사이드 C-K로 전환한다 [47];Bifidobacterium fermentum은 진세노사이드 F2를 진세노사이드 C-K로 전환할 수 있다 [39];항생제의 c-및 C-20 위치 hydrolyzes ginsenoside Rb1 aglycone의 c-위치와 C-20 위치에서 각각 ginsenosides Rd를 생성하 려면 Rg3 [39] 그리고 Gyp-x Ⅶ, F2 키 [40]다.Lactococcus lactis[36]와 Thermus thermophilus[42-43] 로부터 복제된 글루코시다제 유전자는 대장균에서 발현하여 ginsenoside Rb1의 C-20 및 C-3위치의 외부 및 내부 포도당 부분을 점진적으로 가수분해할 수 있는 글루코시다제를 생산하였다.반응은 다음과 같다:Rb1 → Rd → Rg3 (S) 및 F2 → C-K.
In recent years, edible fungi have also been used in the study of the glycosidase hydrolysis of ginseng saponins. For example, Cordyceps militaris can convert ginseng saponin Rb1 to the rare ginseng saponin F2, with the conversion pathway being Rb1→Rd→F2 [44]. The honey ring fungus can convert ginsenoside Rb2 into the rare ginsenosides C-Y and C-K, with the conversion pathway being Rb2→C-Y→C-K [45]. This is the first time in the literature that a basidiomycete has been used to convert ginsenoside Rb2 into the rare ginsenoside C-K.
미생물의 형질전환은 그 자체의 독특한 장점을 가지고있다.반응 조건이 온화하고, 물리적, 화학적 변환 방법과 비교하여 높은 온도와 압력이 필요하지 않아 비용이 절감됩니다.반응 중에는 유기 시약이 거의 사용되지 않아 ginsenosides의 활성을 최대한 보장 할 수 있습니다.미생물이 분비하는 효소는 당이나 단백질 등 불순물을 분해 · 섭취하고, 진세노사이드 농도를 높이며, 전환율을 높인다.미생물 전환 방법은 원료 이용 효율이 높고 전환 효율이 높아 원료를 절약할 뿐만 아니라 [46] 생산량도 증가한다.
2.1.2 ginsenosides의 당군의 효소 가수분해
미생물 전환의 특이도는 직접 효소 전환의 특이도보다 낮으므로 glycosidase의 활성을 조절하여 부산물의 생성을 제한하고 전환의 특이도를 향상시킬 필요가 있다.
사포닌은 구조적 차이와 기능적 다양성을 가지고 있다.인삼 사포닌 구조는 1~4개의 글리코시드 결합을 포함한다.일반적인 설탕 반 족 으로는 β-glucose, L-arabinose D-xylose 그리고 L-rhamnose, 시너지 효과 가 조치를 요구하는 다른 효소들의 bioconversion을 이루는 것이다.일반적인 효소로는 글루코시다아제, 만노시다아제, 아라비노시다아제, 자일로시다아제 등이 있으며, 이들은 주로 미생물이나 동물 · 식물로부터 분리 · 정제된다.진세노사이드의 효소전환연구에서 연구자들은 우선 자연미생물이 생산한 효소를 리용하여 진세노사이드의 글리코시드결합을 가수분해하였다.예를들어, 사용 Monascus purpureus, β를 생산 할 수 있는-glucosidase extracellularly, 발효 하기 ginsenosides 2.3-fold을 달성 ginsenosides에서 Rg3의 대량 부분이 증가 [57]다.추출 연구 진행 되면서, 연구원들은 비교적 순수 한 β-glucosidase에서 곰팡이, 동물과 식물을 hydrolyze ginsenosides다.진 et알다.[58] 사용 β ginsenosides을 변환하는-glucosidase Rb1, Rb2, Rc와 Rd으로 변환 되었희귀 사포 닌 Rh2 사용 β-glucosidase다.그러나 미생물 및 동물, 식물로부터 분리한 효소는 대부분 혼합효소로서 목표한 방식으로 전환하기 어렵고 부반응 생성물이 많아 전환생성물의 분리 및 정제의 어려움이 높아진다.
분자생물학과 유전공학 기술의 발달로 유전자재조합 기술을 이용하여 유전적으로 조작된 세균을 구성하여 인삼 사포닌의 당화를 수행하는 것은 인삼 사포닌의 전환효율을 향상시키는 효과적인 방법이다.성숙한 발현호스트로서 대장균과 효모세포는 종종 재조합 생물학적 효소 단백질의 선호 발현벡터로 사용된다.glycosyltransferase유전자가 벡터 세포에 도입되면 효율적으로 ginsenoside Rh2를 생산한다 [59].최근에는 열성 박테리아로부터 xylosidase 유전자 xln-DT를 유전자 접합 기술을 이용하여 pelB 신호 펩타이드의 하류 pET-20b 플라스미드에 재결합하였다.재조합 플라스미드 pelB-xln-DT는 대장균 발현 숙주인 E. coli BL21 (DE3)로 변화되었으며,이 효소는 노토삼 saponin R1의 글리코시드 결합을 가수분해하는 촉매로 사용되었다.그리고 성공적으로 ginsenoside를 생산했습니다 Rg1 [44]이다.Jeon 등은 재조합 glucosidase (MT619)를 이용하여 ginsenoside Re를 전환하였으며, 전환 경로는 Re →Rg1 →F1 →MT1 이었다 [60].MT1은 ppt 타입의 새로운 진세노사이드이다.유전자를인 코딩 β-glucosidase의 두 가지 변종을에서 대장균 복제었고 매우 대장균에 표현 BL21 (DE3)이다.BL21 (DE3) 원유 추출물을 이용하여 진세노사이드 Rb1을 가수분해하여 진세노사이드 F2 (40);대장균에서 나란히 발현되는 재조합 효소는 순도가 높으며, pp 형 진세노사이드 (ginsenoside)를 희귀한 진세노사이드 Rh2(S)로 전환할 수 있다 [61].
현재 대부분의 연구는 하나의 효소를 이용하여 진세노사이드를 전환시킨다.따라서 향후 연구에서는 유전자 재조합 기술을 이용하여 동일한 숙주에서 서로 다른 기능을 가진 효소를 발현시킬 수 있다.다양한 효소들의 시너지 효과를 통해 특정 요구에 부합하는 희귀 진세노사이드 및 그 유도체를 생산하는 목표를 달성할 수 있으며, 이를 통해 인삼 자원의 이용률을 향상시킬 수 있다.
ginsenosides의 aglycone 구조의 미생물 변형 2.2
ginsenoside 아글리콘의 구조개질에 관한 연구는 주로 ppd 형 ginsenosides에 집중되어 왔으며 25-OH-PPD, 25-OCH3-PPD와 같은 유도체가 얻어졌다.유도방법은 보통 화학적, 물리적 방법이며, 생물학적 방법으로 아글리콘 구조를 변화시키는 연구는 거의 없었다.보고된 주요 방법은 쥐에서 C24-C25위치에서의 이중 결합의 수화이다.의 주요 대사 경로 20S-dammar-24-en-2 α, 3 β, 12 β, 20-tetrol (GP) 관찰은 24의 산화, 25-double 본드 24을 만들 려면이 25-epoxide, 뒤이어 지구와 20을 만들 려면이 재배치 가 24-epoxide (그림 3) [62].연구자들은 인삼 사포닌과 동맥 (Cordyceps militaris)의 공동 함양을 이용하여 ginsenoside Rg1을 25-OH-(S/R)-Rh1로, panaxoside R1을 25-OH-20(S/R)-R2로 전환하였다.전환 산물 중 25-OH 유도체의 함량은 ginsenoside Rh1 및 panaxoside R2보다 훨씬 높아 유도체의 분리 및 정제가 용이하다 [63-64].Mucor spinosus를 20(S)-protopanaxatriol과 공동 재배하여 6개의 유도체를 얻었다.연구 결과, C-12위치에서의 탈수소화에 이어 C-7 또는 C-11위치에서의 추가적인 하이드록실화와 C-15위치에서의 카보닐화, 그리고 C-26위치에서의 이중결합 재배열에 의해 생성된 진세노사이드 유도체가 암세포에 대해 상당한 억제 활성을 가지고 있음이 증명되었다 [65].
국내외 연구결과에 의하면, 이것이 ginsenosides의 지역적으로 선택적인 hydroxylation에 가장 효과적인 생물촉매 시스템일 것으로 추측된다.실험 연구 결과 이들 유도체는 다양한 메커니즘을 통해 생체 내 및 체외에서 서로 다른 효과를 발휘하며, 이들의 생물학적 활성은 일반적인 진세노사이드 (ginsenosides)보다 높다는 것이 밝혀졌다 [66].예를 들어, Rb1은 탈수소 반응을 거쳐 dihydroginsenoside Dg-Rb1을 형성하는데,이 Dg-Rb1은 전신의 매개변수에 영향을 미치지 않고 손상된 뉴런을 회복할 수 있으며, Dg-Rb1의 유효량은 Rb1보다 10배 낮다 [67].ginsenoside Rh2의 옥틸 에스테르 유도체 Rh2-O는 내재적 세포사멸 경로를 활성화시킴으로써 Rh2보다 높은 항암 활성을 가진다 [68].PPD의 아세틸 유도체는 상당한 항증식 및 세포자멸사 유도 활성이 있으며, 일부 유도체는 PPD보다 높은 항암 활성을 가지고 있다 [69].pyrazine ring을 25-OH-PPD에 도입하여 항암 활성을 향상시켰다.2-피라진-ppd는 위암세포의 증식을 현저히 억제할 수 있으며 정상세포에 대한 독성이 거의 없다 (인간의 위상피세포주 GES-1) [70].아글리콘 PPD의 유도체 25-OH-PPD는 진세노사이드 Rg3, 파클리탁셀, 아미놀레불린산 [71]과 같은 시판 중인 기존 약물보다 항암 활성이 좋다.
따라서 ginsenoside의 원래 활성 구조를 유지하면서 극성 그룹과 약리 그룹을 도입하여 ginsenoside의 수용성, 표적 및 효능을 향상시키고 ginsenoside의 생물학적 이용성을 향상시키기 위해 aglycone 구조를 변형할 수 있습니다.
ginsenosides의 당화 2.3
2,3-옥시도스콸렌으로부터 시작하여,의ginsenosides의 생합성3단계로 나눌 수 있다:2,3-옥시도스쿠알렌 사이클라제 (OSC) 사이클리즈 2,3-옥시도스쿠알렌;그 후 히드록실화와 당화 반응은 사이토크룸 (Cyt)과 글리코실트랜스페라제 (GT)에 의해 수행되어 궁극적으로 진세노사이드 (ginsenoside)를 생성한다 [72].UGT 효소는 생물체의 희귀 진세노사이드 합성에 가장 중요한 효소 중 하나이며 [73] 진세노사이드 생합성의 마지막 단계이기도하다.UGT 유전자는 Lactobacillus rhamnosus 로부터 클로닝 되어 E. coli BL21 (DE3)에서 발현되었다.재조합 UGT 단백질은 Rh2를 glucosylated ginsenoside Rh2와 diglucosylated ginsenoside Rh2 [74] 라는 두 개의 새로운 진세노사이드로 변환시킬 수 있다.
트리테르페노이드 아글리콘은 UGT에 의해 촉매되어 구조가 다른 진세노사이드를 형성한다.프로토파낙사디올형 아글리콘은 C-3, C-20위치에서 당화되며, 프로토파낙사디올형 아글리콘은 C-6, C-20위치에서 당화된다 [80].그림 4에 드문 ginsenoside glycosylation 경로가 나와 있습니다.Arabidopsis thaliana에서 glycosyltransferase 73C5 (UGT 73C5)를 분리하여 PPD에 단계적 첨가 하였다.이 glycosyltransferase는 PPD의 C-3 hydroxyl group에 선택적으로 포도당을 이동시켜 ginsenoside Rh2를 합성할 수 있으며, 보고된 가장 큰 ginsenoside Rh2 수율을 달성하였다 (3.2 mg/mL) [75].글리코실트랜스페라제74AE2 (UGT 74AE2)는 포도당이 PPD와 C-K의 C-3 하이드록시기로 이동하는 것을 촉매하여 [76] 각각 Rh2와 F2를 형성한다.글리코실트랜스퍼라제94Q2 (UGT 94Q2)는 포도당을 Rh2와 F2로 전달하여 각각 Rg3와 Rd를 형성할 수 있다 [77].UGT51은 Saccharomyces cerevisiae S288c [78]의 glycosyltransferases 중 하나로, 포도당을 PPD의 C-3 히드록시기로 이동하여 Rh2를 형성할 수 있다 [79].UGTs에 대한 향후 연구는 ginsenoside glycosylation의 조절 메커니즘에 대한 통찰력을 제공하고 ginsenoside 생산을 수정하는 새로운 방법을 제시할 수 있을 것이다.
진세노사이드 형성을 촉매하는 직접인자로서 UGTs는 생체분해에 의한 진세노사이드 생성에 필수적인 역할을 한다.대부분의 식물유래 UGTs는 촉매 활성이 낮은 반면, 재조합 미생물 UGTs는 미생물 기질 세포에서 기질 문란 및 높은 발현 수준 등 특별한 생체 촉매 특성을 가지고 있어 진세노사이드 생산에 효과적인 도구이다.따라서 목표 희귀 진세노사이드의 생산 및 수율을 높이기 위해서는 UGTs의 촉매 활성을 향상시킬 필요가 있다.
결론 및 전망 3
Studies have shown that rare ginsenosides have higher medicinal value다.이와 동시에 낮은 수용성과 낮은 희귀진세노사이드 함량으로 인해 적용에 한계가 있었다.다양한 미생물의 세포내 또는 세포외 효소에 의한 ginsenosides의 가수분해 또는 당화는 polysacchride ginsenosides와 비활성 aglycones를 희귀한 ginsenosides로 효과적으로 전환시켜 ginsenosides의 생물학적 이용성을 향상시킨다.
연구에 따르면 일부 기능군의 변화는 분자 구조와 특성을 변화시킬 수 있으며 이로 인해 수용체에 대한 약물의 결합에 영향을 미치고 효능에 영향을 미치는 것으로 나타났다.예를 들어, 알킬기는 화합물의 지질 용해도를 증가시키고, 해리성을 감소시키고, 안정성을 증가시키고, 약물의 작용 기간을 연장시킬 수 있고;sulfhydryl 그룹은 지질 용해도를 증가시키고 약물 흡수를 용이하게 한다;아미드 결합은 생물학적 거대 분자와 쉽게 수소 결합을 형성하고 수용체에 결합하여 특별한 구조적 특이성을 보일 수 있다;그리고 수소결합을 형성하기 위해 히드록시기가 깨지면 화합물의 수용성이 증가하므로 약물의 활성이 증가한다.

ginsenosides의 구조로 볼 때, C-2, C-11, C-15, C-24, C-30위치에서 히드록실화 반응이 일어날 수 있다고 추측된다;C-12 및 C-13위치의 탄소-탄소 이중결합은 첨가반응과 산화반응을 겪을 수 있다;동시에, diol-type ginsenosides는 C-12 및 C-24위치에서 산화되어 oryctol-type ginsenosides를 형성 할 수있다.따라서 진세노사이드의 구조를 변형시킬 수 있는 효소를 여러 가지 미생물과 효소의 스크리닝을 통해 찾아내고, 기존의 희귀 진세노사이드의 활성 구조를 바탕으로 일부 그룹을 첨가하거나 knockout 할 수 있다면, 진세노사이드의 약리학적 활성과 타겟이 향상될 수 있으며, 진세노사이드의 생물학적 이용성이 증대되어 진세노사이드의 구조 변형시 새로운 방향을 제시할 수 있을 것이다.
At the same time, with the continuous development of technology in the fields of food, medicine, the continuous development of technology in the fields of food, medicine, and biochemistry, researchers can use genetics, molecular cytology, and other interdisciplinary integration, as well as high-throughput screening and genomics technology to select or design enzymes or strains with high selectivity and conversion rates. Biological means can be used to achieve the industrial 생산of highly active rare ginseng saponins and their derivatives, further increasing the yield of rare ginseng saponins and their highly active derivatives. This is of great significance 을making full use of ginseng resources for the benefit of the public.
참조:
[1] 김진희 (Jin Hee Kim), 김미선 (Miseon Kim), 윤선미 (Sun-Mi Yun) 외Ginsenoside Rh2는 HEC1A와 Ishikawa 자궁내막암세포에서 세포사멸을 유도하고 상피-중간엽 전이를 억제한다 [J].Biomedicine &96 Pharmacotherapy, 2017년,이다.871-876다.
[2] Jiang Z, Yang Y, Yang Y 외.Ginsenoside Rg3는 PD-L1을 하향조절하고 면역을 재개함으로써 폐암에서 시스플라틴 저항성을 약화시킨다 [J].생물 의학이다.Pharm. 2017.96.378-383.
[3] 야 오 밍 W, Guan Y. Ginsenosides in 암: 한 집중 on the 규정 of 셀 신진대사를 활발하다. 생물 의학 Pharmacother다. 2022 10월 10; 156:113756.doi:10.1016/j.biopha.2022.113756.
[4] Yu H, 왕Y, Liu C, 외.FeCl3 촉매작용에 의한 Ginsenoside Rb1의 6가지 형태의 Highly Bioactive Ginsenoside Rg3 및 그 유도체로의 전환 (Conversion of Ginsenoside Rb1 into Six Types of Highly Bioactive Ginsenoside Rg3 and 의Derivatives by FeCl3 Catalysis)Chem Pharm Bull (도쿄).2018년; 66 (9):901-906다.
[5] Zhang J,Ai Z, Hu Y, 외.연구논문:널리 표적화된 대사체분석에 기초한 상용살균법이 신선인삼 과육의 ginsenosides 형질전환에 미치는 놀라운 영향 (Remarkable impact of commercial sterilizing on fresh 인삼 과육의 ginsenosides transformation based on 폭넓게 targeted metabolomics analysis)Food Chem X. 2022 Aug 9;15:100415.
[6] 하세가와 히데오, 성, 외.장내세균에 의해 형성된 인삼 사포닌 대사 산물이 주요.Planta Medica, 1998, 62(5), 453-457.
[7] 하세가와, 히데오, Sung, 외.인삼을 가수분해하는 사람의 장내 Prevotella oris의 역할 Saponins다.Planta Medica, 1997년, 63 (5), 436-440.
[8] SHANGGUAN lihua, 류 guoquan다.인삼 성분의 대사에 관한 연구 진행 [J.「 Chinese Traditional and Herbal Drugs 」, 1999(11):865-870.
[9]. 리 김병훈, 리, 상준희 외, 『 사회복지실천기술론 』, 학지사Novel의 In vitro Antigenotoxic Activity 인삼 사포닌 대사산물은 장내 세균에 의해 형성된다.플란타 메디카, 1998, 64(6), 500-503.
[10] Yoshimasa 야마구치, Masaya Higashi, Hideshi 고바야시다. 효과 of ginsenosides on 장애 가 있는 성능 야기 byscopolamine은 쥐 [J.European Journal of Pharmacology, 1996, 312(2):149-151.
[11] Kim WY, Kim JM, Han SB 등.인삼을 고온에서 찌면 생물학적 활성이 강화된다.J Nat Prod, 2000, 63(12):1702-1704.
[12] Guo HY, Xing Y, Sun YQ, 외.20(R)-panaxotriol 로부터 합성된 Ginsengenin 유도체:HIF-1 경로를 대상으로 하는 합성, 특성 및 항암 활성.J 인삼 Res. 2022 Nov;46(6):738-749.
[13] 김고, 김은, 송기 외.맹장 결찰과 Puncture-Induced Sepsis에 대한 희귀 Ginsenoside Rg4의 억제 활성.IntJ Mol Sci. 2022 16;23일 (18):10836.doi:10.3390/ijms231810836.
[14] 천즈, 왕 G,시 X 외.Ginsenoside Rg5는 P2RY12와 동종적으로 상호작용하며 호중구 네토시스 및 염증 반응에 대응함으로써 심부 정맥 혈전증을 개선합니다.앞 Immunol다. 2022년 8월 12일;13:918476.
[15] 류 yannan다. 진세노사이드 Rg5의 준비와 항위 및 유방암 활성 [D].산시:서북대학, 2019.
[16] 등제이, 류이, 두안 Z G 등.Protopanaxadiol과 protopanaxatriol-type saponins은 고지방식이/streptozocin-induced mice에서 제2 형 당뇨병의 포도당과 지질대사를 개선시킨다 [J].프론트 파솔,2017, 8:506.
[17] MAENG Y S, MAHARJAN S, KIM J H, 외.ginsenoside인 Rk1은 액틴 구조 리모델링을 통해 작용하는 혈관 누출의 새로운 차단제이다 [J], PLoSOne, 2013, 8(7):e68659.
[18] RYOO N, RAHMAN MA, HWANG H, 외.Ginsenoside Rk1은 배양된 쥐 해마 신경세포에서 NMDA 수용체의 새로운 억제제이다 [J].J 인삼 Res, 2020, 44 (3):490-495.
[19] OH J M, LEE J, IM W T, 외.Ginsenoside Rk1은 미토콘드리아 막 전위 소실과 카스파스의 활성화를 통해 신경모세포에서 세포사멸을 유도한다 [J].Int J Mol Sci, 2019, 20(5):1213.
[20] SIDDIQI M H, SIDDIQI M Z, AHN S, 외 ginsenosides Rg5:Rk1의 murine osteoblasticMC3T3-E1세포에 대한 자극효과 (J.Phytother Res, 2014, 28(10):1447-1455.
[21] 크리시카 삼비알, 라훌비 크람 싱.미생물의 biotransformation에 의한 testosterone의 생산양상과 향후 전망.스테로이드, 2020, 159(C).
난보, 유잉, 왕우산 등 [22] Ginsenosides의 미생물 형질전환 연구 진행.식품연구 개발, 2017, 38(14):196-199
[23]ZHOU Zhong-liu, 리Chun-얀,CHEN Lin-hao1 등.Natural의 Biotransformation Saponins다 [J다]Chinese Journal of Experimental Traditional Medical Formulae, 2019, 25(16):173-192.
[24] M. J. H, 배은아, 민경 외.인체 장내세균에 의한 20(S)-및 20(R)-Ginsenoside Rg3의 대사와 in Vitro 생물학적 활동과의 관계 (J).Biol다.Pharm Bull, 2002, 25(1):58-63.
[25] 한강 mingxin, LI fangtong, 장 yan, et 알다. Biotransformation of Rare Protopanaxadiol Saponinby 인간 장내 Microflora다 [J다]Chemical Journal of Chinese Universities, 2019, 40(07):1390-1396.
장옌, 이방동, 한민신 외, RRLC-Q-TOF MS 및 UPLC-QQQ MS에 의한 인간 장내 Protopanaxatriol 사포닌의 대사산물 분석.중국질량분석학회 Journal of Chinese Mass Spectrometry Society, 2020, 41(01):66-75.
[27] TANG lan1, FU lulu,, SHEN liting, et알다.vitro에서 쥐의 장균에 의한 파낙스 노토삼의 총 사포닌의 분해.「 Chinese Traditional and Herbal Drugs 」, 2018, 49(02):396-399.
[28] Guo Y P, Chen M Y, Shao L, 외.HPLC-MS/MS에 의한 체내 장내 미생물 매개 biotransformation을 통한 rat 혈장내 Panax noto인삼사포닌 대사산물의 정량 (J.Chinese Journal of Natural medicine, 2019, 17(3):231-240.
[29]CHEN sijian, WU dongxue, LIU suying 외.진세노사이드 (J) 중국 전통 특허 약물의 화학적 및 생물학적 변질의 진보,2022, 44(5):1539-1545.
[30] 왕샨샨, 후핑, 유샤오원.천연물의 생물형질전환 연구 진행.한국신약학회지, 2016, 25(1):71-75.
[31] 가오후안, 저우안동, 위안예 외.Aspergillus niger sp. J7[J]에 의한 Compound K 제조를 위한 Ginsenoside Rb1의 효소분해.현재 생명공학, 『 한국정치학회보 』 2016, 6(02):98-104.
[32] 송 X L, 우 H, 피아오 X C 등.파낙스 인삼 첨가 뿌리에서 추출한 ginsenosides의 미생물 형질전환 (Microbial transformation of ginsenosides extracted from Panax ginseng advential roots in an airlift bioreactor[J])한국생명공학전자학회지, 2017, 26:20-26.
[33] Yan Q, Zhou W, Shi X L, 외.compound K 로의 ginsenoside Rb1의 Biotransformation pathways by 곰팡이에서 β-glucosidases Paecilomyces Bainier sp. 229 [J], 프로세스 생화학, 2010년, 45 (9):1550-1556.
[34] 후 Y B, 왕엔, 얀 X C 외.Ginsenoside Re impacts on biotransformationproducts of Ginsenoside Rb1 by Cellulosimicrobium cellulans sp. 21 및 그 기작 [J], 공정생화학, 2019, 77:57-62.
[35] Jitendra Upadhyaya, Min-Ji 김,Young-Hoi Kim 외.부제:효소formation of compound-K from ginsenoside Rb1 by enzyme preparation from cultured mycelia of Armillaria mellea[J]인삼연구지 2016, 40(2):105-112.
[36] 리링,리 Soo Jin, Yuan Qiu Ping, 외 알다.생리 활성 생산 재조합 Lactococcus lactis[J]를 이용하여 ginsenoside Rg3(S)와 compound K.인삼연구지 2017, 42(4):412-418.
이효진 (Hyojin Lee), 안승일 (Seung Il Ahn), 양병욱 (Byung Wook Yang) 외산삼에서 어육장 유래 젖산균에 의한 Ginsenosides의 Biotransformation에 관한 연구 (J.「 Microbiology and Biotechnology Letters 」, 2019, 47(2):201-210.
[38] 류 C Y, 주오 K Z, 유 H S 등.특집 ginsenosidase type-I에 의한 노토삼 잎 ginsenosides C-Mx 및 C-K의 제조 (Preparation of minor ginsenosides C-Mx and C-K from noto삼 잎 ginsenosides by a special ginsenosidase type-I[J.공정생화학, 2015, 50(12):2158-2167.
[39] 장 R, 황 X M, 얀 H J 외.을 이용하여 C-3 Glycoside에서 Glucose를 가수분해하여 Ginsenoside Rd 로부터 Compound K를 고선택적으로 생산 β-Glucosidase의 Bifidobacterium breve ATCC 15700다 [J다]한국미생물 · 생명공학회지 2019년, 29(3):410-418.
[40] Almando Geraldi, 니 matuzahrohabet, Fatimahab, 알다. Enzymatic biotransformation of ginsenoside Rb1 by 박테리아의 재조 합 β-glucosidase 인도네시아에서 [J]과 격리 되어 있다.Biocatalysis and Agricultural Biotechnology. 2020, 23(C):101449-101449.
[41] Li L, Lee S J,Yuan Q P, 외.생리활성 ginsenoside Rg3(S)의 생산 및 재조합 Lactococcus lactis[J]를 이용한 화합물 K.인삼연구지 2017, 42(4):412-418.
[42] 페이 J 제이,시 J C,인 R 외.GH3에 의한 ginsenoside Rb1의 효소적 전환 ginsenoside 20(S)-Rg3 β-glucosidase Thermotogathermarum에서 충족시 켜야 한 5069 T [J].Molecular Catalysis B:Enzymatic 논문집 2015년, 113:104-109.
[43] Zhang S H, Xie J C, 자 오L G. Cloning, overexpression and 성격 묘사of a thermostable β-xylosidase Thermotoga에서 petrophila and cooperative transformation of ginsenoside extract to ginsenoside 20(S)-Rg3 with a β-glucosidase다 [J다]생물유기화학 (Bioorganic Chemistry), 2019, 85:159-167.
[44] 114-120다. [리 qi, 통 xinyi, 지 앙 yujie, et 알다. 건설 of 전체 cell 촉매 pelB-Xln-DT and its 응용 프로그램 Panax notoginsenoside R1의 biotransformation에서 [J.한국산림공학회지 2020년, 5(04):114-120.
[45] 김민지 (Min-Ji Kim), 지텐드라 우파드야 (Jitendra Upadh ya), 민선윤 외.에 의한 화합물 Y와 화합물 K 로의 ginsenoside Rb2의 Highly regioselective biotransformation 균 사체를 정화 β-glycosidase에서 Armillaria mellea다 [J다]인삼연구지 2017, 42(4):504-511.
[46] 종구 yating다.인삼의 선별 사포 닌 변환 변종 GsBt3 and Its 변환 총으로 Saponins 파낙 스의 [D] quinquefolium 합니다.상하이:상하이사범대학, 2012.
[47] 양위안차오, 왕잉핑, 옌메이샤 외.ginsenoside compound K 생산에 의한 식물병원성 곰팡이의 스크리닝 (J.China Journal of Chinese Materia Medica, 2011, 36(12):1596-1598.
[48] 천양, 장음메이핑, 왕이 외.미생물 변형 ginsenoside Bacillus subtilis [J]에 의한 Panax 인삼의 총 사포닌으로부터 Rg3.리시젠의학과 모체연구, 2014, 25(11):2676-2678.
[49] 진옌, 진상미, 인청리 biotransformation of major ginsenoside Re to minor ginsenoside Rh1by Sphingomonas sp. 2-f2 [J].연변대학농학회지 2011, 33(02):103-107.
[50] 량지치, 장징루, 정혜주 외.진세노사이드 Rg3의 Rh2로의 미생물학적 형질전환 (J.인삼연구, 2018, 30(03):6-10.
[51] 얀 Q, 조우 W,시 X L 외.compound K 로의 ginsenoside Rb1의 Biotransformation pathways by 곰팡이에서 β-glucosidases Paecilomyces Bainier sp 229 [J].공정생화학, 2010, 45(9):1550-1556.
[52] 예 L, 저 C Q, 저 W 등.highly substrate-tolerant Paecilomyces bainier 229-7에 의한 ginsenoside Rb1의 ginsenoside Rd 로의 생물학적 전환 (J.바이오원천기술, 2010, 101(20):7872-7876
[53] 천샤오춘, 다이주, 푸룽자오.희귀 ginsenoside Rh2의 생물촉매 합성 (J.장시화학공업, 2019(02):55-57.
[54] Su J H, Xu J H, Lu W Y, 그 외.새로 분리한 Fusarium proliferatum ECU2042를 이용한 ginsenoside Rg3의 Rh2로의 효소적 전환 (J.한국분자촉매 B 효소학회지 2006, 38(2):113-118.
[55] Su J H, Xu J H, Yu H L, 그 외.소설의 특성 로 전환하는 β-glucosidasefrom Fusarium proliferatum ECU2042 ginsenoside Rg3 Rh2다 [J다]한국분자촉매 B 효소학회지 2009, 57(1-4):278-283.
[56] 우 xiuli, WANG yan, ZHAO wenqian 외.진세노사이드 (ginsenoside) Rg3의 균사생물형질전환 [J.Acta Microbiologica Sinica, 2008(09):1181-1185.
[57] 콩여이, 손지아, 유엔 외.Monascus purpureus에 의해 발효된 ginsenoside Rg3의 형질전환에 관한 연구 (J.중국의 전통 및 약초, 2018,49(06):1298-1303.
[58] 진 f.x.제2회 국제자연의학 및 미생물 심포지엄에서는 [M.Tokyo, Japan 1998, Oct, 24-26:1-15.
[59] 주앙이, 양그이, 첸 X H 외.주요 난잡미생물 효소인 repurposing을 통한 효모에서 식물유래 ginsenoside Rh2의 생합성 (Biosynthesis of plant derived ginsenoside Rh2 in yeast via repurposing)대사공학, 2017, 42:25-32.
[60] 전병민 (Byeong-Min Jeon), 백종인 (Jong-In Baek), 김민성 (Min-Sung Kim) 외Protopanaxatriol-Type Ginsenosides Re[J]의 효소적 Transrhamnosylation에 의해 생성된 새로운 Ginsenoside MT1의 특성 (characteristics of Novel Ginsenoside MT1 Produced by an enzyme Transrhamnosylation of Protopanaxatriol-Type Ginsenosides Re[J.Biomolecules. 2020, 10(4):525-525.
[61] 무하마드 주바이르 시디키, 히폴리토 아마랄 시메네스, 송봉규 외.Saccharibacillus kuerlensis에서 클로닝된 BglSk를 이용한 ppd 형 주요 ginsenosides 로부터 ginsenoside Rh2(S)의 생산을 2개의 glycosidase와 함께 시리즈 [J]로 향상시켰다.사우디 생물과학 저널 2021, 04, 079.
[62] Chen H, Dong, Zhi F 등.발견, 합성 및 structure-activity의 관계 20S-dammar-24-en-2 α, 3 β, 12 β, 20-tetrol (GP) 파생상품 AMPK의 새로 운 계급 으로서 α 2 β 1 γ 1 activators다 [J다]Bioorganic &약용화학, 2016, 24(12):2688-96.
[63] 신 S, Jl A, 유 X아 외.Cordyceps Sinensis-ScienceDirect에 의한 20(S/R)-Rh1 유도체의 ginsenoside Rg1 to 25-OH 유도체의 Highly regioselective biotransformation (J.Bioorganic &약용화학편지. 2020, 30(21):127-504.
[64] Liu J S, Yu X N, Qiu Z D, et al.Cordyceps sinensis를 매개체로 한 notoginsenoside R1의 DOXinduced cell 손상에 대한 심장 보호 효과가 상승된 25-OH-20(S/R)-R2로의 생체 변환.RSC 발전, 2022, 12, 129-38.
[65] 첸 G T,지 H J, 송 Y 등.Mucor racemosus에 의한 20(S)-protopanaxatriol의 생물형질전환 및 일부 산물의 항암활성 (J.Biotechnology Letters, 2015, 37(10):2005-2009.
[66] Kim M Y, Cho J Y. 20S-dihydroprotopanaxadiol, ginsenoside 유도체는 단핵구 및 대식세포의 선천적 면역 반응을 증진시킨다.인삼연구지 2013, Jul, 37(3):293-9.
[67] 아카나카 M, 주 P, 보 Z 외.dihydroginsenoside Rb1을 정맥 주입시 VEGF와 Bcl-XL의 상승작용을 통해 압축성 척수 손상과 허혈성 뇌 손상을 예방한다.J 신경외상, 2007, 24(6):1037-1054.
[68] 첸 F, 정 S L, 후 J N,외.Ginsenoside Rh2의 옥틸에스터는 외생세포사멸 경로를 활성화하고 Akt/p38 MAPK 신호전달 경로를 조절함으로써 인간 hepg2cell에서 세포사멸 및 G1세포주기 정지를 유도한다 [J].Journal of Agricultural &Food Chemistry, 2016, acs.jafc., 6b03519.
[69] 두 G J, 다이 Q, 윌리엄스 S 외.protopanaxadiol 유도체의 합성 및 항암활성 평가 (Synthesis of protopanaxadiol derivatives and evaluation of their anticancer activity) 항암제, 2011, 22(1):35.
[70] 신규 dammarane 유도체인 Xu D, Tao L, Yan L, et al. 2-Pyrazine-PPD는 위암세포에서 reactive oxygen speciesmediate apoptosis와 endoplasmic reticulum stress에 의한 항암활성을 보였다.European Journal of Pharmacology, 2020, 881 쪽.
[71] 위암의 잠재적 치료제로서 새로운 ginsenoside 유도체인 Xu D, Yuan Y, Fan Z 등 4-XL-PPD는 반응성 산소종의 세포사멸을 유도하고 이동성 및 침습성 (J)을 억제하는 것을 통해 항암 활성을 보인다.Biomedicine &약물치료, 2019, (118):108.
[72] Li Y, Baldauf S, Lim E K 외.연구논문:Arabidopsis thaliana의 UDP-glycosyltransferase 다유전자군의 계통학적 분석 (J.한국생물화학학회지 2001, 276(6):4338.
[73] 크리스텐슨 L P. Ginsenosides:화학, 생합성, 분석 및 잠재적 건강 효과 (1장)[J].Adv Food Nutr Res, 2008, 55(55):1-99.
[74] 왕 D D, Yeon-Ju Kim, 남 씨는 백, et al. ginsenoside의 Glycosyltransformation에 대한 자료입니다 Rh2 into 두 소설 ginsenosides Lactobacillus rhamnosus 로부터 재조합 glycosyltransferase를 이용한 실험과 이의 in vitro 이용 [J.인삼연구저널 2021 45(1):48-57.
[75] Hu Y, Xue J, Min J 등.연구논문:Arabidopsis thaliana glucosyltransferase-catalyzed coupled reactions을 이용한 ginsenoside Rh2의 생체촉매 합성 (J.한국생명공학회지, 2020, 309:107-112.
[76] 정 S C, 김 W, 박 S C 외.두 가지 인삼 UDP-glycosyltransferases 가 ginsenoside Rg3와 Rd.[J.식물 &세포생리학, 2014, 55(12):2177-88.
[77] Khorolragchaa, Altanzul, 김, et al. 그룹 화 and characterization 의 추정 되는 glycosyltransferase 유전자 from Panax 인삼 마이어 [J]이다.Gene, 536(1):186-192.
[78] Warnecke D, Erdmann R, Fahl A 외.Saccharomyces cerevisiae, Candida albicans, Pichiapastorisand Dictyostelium discoideum 으로부터 sterol glucosyltransferases를 encoding 하는 UGT 유전자의 Cloning 및 기능성 발현 (J.J Biol Chem, 1999, 274(19):13048-13059. [79] 주앙이, 양그이, 첸 X H 외.주요 난잡미생물 효소인 repurposing을 통한 효모내 plant-de-rived ginsenoside Rh2의 생합성 (Biosynthesis of plant-de-rived ginsenoside Rh2 in yeast via repurposing)Metab Eng, 2017, 42:25-32.
[80] 자 오 J N, Wang R F, Zhao S J, et al. 미리 in glycosyltransferases, the important bioparts for production of 다양 한 ginsenosides다 [J다]Chinese Journal of Natural medicine, 2020, 18(9):643-658.
-
Prev
Natural Black Rice Extract Anthocyanins: Antioxidant Product Solutions
-
다음
희귀 Ginsenoside Rg1 Rb1 Rg3에 관한 연구


 영어
영어 프랑스
프랑스 스페인
스페인 러시아
러시아 한국
한국 일본
일본




