피부에 히알루론산의 용도는 무엇인가요?
루 론 산피부조직과 결합조직을 포함한 인체의 다양한 조직에서 널리 발견되는 흔한 다당류이다.1934년 Meyer 등에 의해 소의 유리체로부터 처음 분리된 이후 히알루론산의 다양한 기능이 발견되었다.히알루론산은 친수성, 점탄성, 생체 적합성 및 면역 원성의 부족으로 인해 국소 약물 전달 시스템, 상처 치유, 질병에 대한 장벽 치료 및 염증 질환의 치료에 응용되고 있습니다.
물리적, 화학적 성질 1
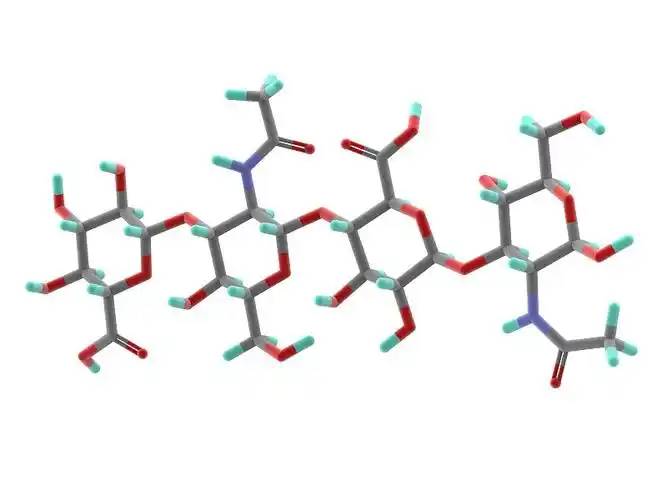
Hyaluronic acid is 한linear polysaccharide polymer composed 의D-glucuronic acid and N-acetylglucosamine, with 이molecular formul한(C₁₄H₂₁NO₁₁)_n. Based on its molecular weight, hyaluronic acid can be classified in을high-, medium-, and low-molecular-weight types. Most 의the properties 의hyaluronic acid are related to its molecular weight. High-molecular-weight hyaluronic acid (HMW-hyaluronic acid) h로한molecular weight range 의103–104 kDa, medium-molecular-weight hyaluronic acid has a molecular weight range of 200–103 kDa, and 저분자 히알루론산 (LMW-hyaluronic acid) has a molecular weight range of 10–200 kDa. Through hyaluronidase, mechanical force, oxidative stress, and other regulatory processes of hyaluronic acid degradation and metabolism, high-molecular-weight hyaluronic acid can be degraded into hyaluronic acid polymers (또는fragments) of different sizes. Low-molecular-weight hyaluronic acid can also be de novo synthesised by hyaluronic acid synthase during inflammatory processes [1]. In the human body, hyaluronic acid typically exists 에서a high-molecular-weight form with a size of approximately 104 kDa. It can bind to water equivalent to 1,000 times its own weight through hydrogen bonds [2] and achieve moisturising effects by reducing water evaporation and inducing hydration of the stratum corneum.
2 생물학적 특성
2. 1 Biocompatibility
Unlike collagen, which is highly allergenic, hyaluronic acid lacks antigenic epitopes [3], making it safer as a topical drug matrix. Another advantage of hyaluronic acid is that it can be rapidly degraded by hyaluronidase when adverse events occur [4]. Different molecular weights also influence the biological properties of hyaluronic acid. High-molecular-weight hyaluronic acid has higher viscosity, longer retention time, and better biocompatibility; low-molecular-weight hyaluronic acid exhibits the opposite characteristics [5].
2.2조직 회복 효과
When inflammation occurs or trauma forms, topically applied high-molecular-weight hyaluronic acid binds with its receptor CD44 to form a hyaluronic acid-CD44 complex, which may trigger a series of reactions 에서fibroblasts, such as changes in the cellular cytoskeleton and regulation of the tissue healing process [6]. During trauma, hyaluronic acid promotes fibroblast migration to the wound site via CD44 expression on fibroblast cells, thereby facilitating tissue healing. However, the receptors of small-molecule hyaluronic acid differ from those of large-molecule hyaluronic acid, and thus this 효과is not observed.
작은 분자 히알루론산홍보 할 수 있-dopa 인산 화하고 활성화 phospholipase PLC γ 1, 그렇게 함 으로써 활성화 산화효소 C는 단백질 (PKC) 신호 전달 경로와 mitogen-activated 단백질 산화효소 (MAPK) 신호 전달 시스템, 체세 포 분열을 조장의 피 기능 세포라 혈관, 혈관 신생 홍보, 수리 및 촉진 조직 [6].
Komorowicz et al. [7] reported that hyaluronic acid with molecular weights of 500 kDa and 1500 kDa caused fibrin to form lateral cross-links rather than branches, thereby altering the fibrin aggregation pattern and inhibiting fibrinolysis; furthermore, on the surface of fibrin clots, 500 kDa and 1500 kDa hyaluronic acid significantly inhibited tissue plasminogen activator (tPA)-catalysed plasminogen activation; therefore, in tissue injury and inflammation, hyaluronic acid can stabilise fibrin by altering its structure and solubility.
2. 3 염증에 대한 조절 효과
In most studies, high-molecular-weight hyaluronic acid exhibits anti-inflammatory effects when applied topically, while lower-molecular-weight fragments exhibit pro-inflammatory effects. This is primarily due to different receptors on the 셀surface for hyaluronic acid of different molecular weights, with high-molecular-weight hyaluronic acid primarily binding to CD44 and lower-molecular-weight hyaluronic acid primarily binding to toll-like receptors (TLR) [5].
High-molecular-weight hyaluronic acid binds to CD44 to form a hyaluronic acid-CD44 complex. The signal transduction cascade triggered by CD44 includes PI3K, PDK1, AKT, and the Ras phosphorylation cascade involving RAF1, MEK, and ERK1/2, thereby reducing inflammatory responses and inhibiting the production of reactive oxygen species (ROS). When inflammation occurs, the production of hyaluronic acid synthase increases, leading to enhanced de novo synthesis of small-molecule hyaluronic acid. Concurrently, under the influence of ROS or enzymatic actions such as hyaluronidase, more large-molecule hyaluronic acid is degraded into small-molecule hyaluronic acid. However, simultaneously, CD44 regulates inflammatory responses by downregulating TLR-4 expression. During this process, as large-molecule hyaluronic acid is degraded, ROS are also cleared, exerting an antioxidant effect. Additionally, hyaluronic acid regulates the expression of inflammatory cells, antigen-presenting cells, dendritic cells, and macrophages at the site of inflammation through CD44, exhibiting anti-inflammatory effects [8–11].
In the interaction between small-molecule hyaluronic acid and TLR, TLR-2 and TLR-4 activate NF-κB protein through Myeloid Differentiation Factor 88 (MyD88)-dependent and MyD88-independent pathways, exhibiting pro-inflammatory effects. In the MyD88-independent pathway, hyaluronic acid increases the expression of interferon-induced pro-inflammatory genes through type I interferon [9].
3 임상 적용
3.1 국소 약물 전달 시스템
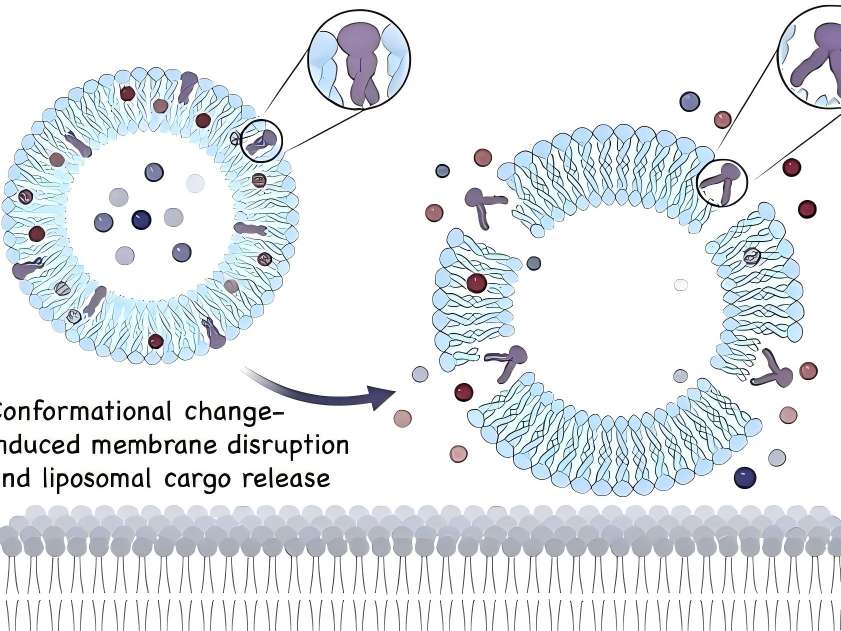
In topical drug formulations for skin diseases, liposomes containing hyaluronic acid are present on the skin surface. Hyaluronic acid can act as a mucosal adhesive agent when the drug takes effect or is absorbed. Additionally, as a topical drug formulation matrix, hyaluronic acid can prolong drug retention time [12].
프리드리히et al. [13] conducted experiments on regulating inflammatory responses associated with acute injury. The combination of high-molecular-weight hyaluronic acid gel with a monoclonal antibody that antagonises TNF-α influenced the bioavailability of the monoclonal antibody, prolonging the drug' 염증부위의 s 작용시간, 약물거주시간을 증가시키며 그럼으로써 상처치유를 더욱 효과적으로 촉진시킨다.여기서는 점막 접착제로 작용하여 약물 흡수를 도울 뿐만 아니라 드럭&를 변화시킵니다#39;s 거주 시간.더 많은 약물에서, 히알루론산의 그러한 효과는 더 설명될 수 있다.
와 함께 3% 디클로페낙 겔2.5% high-molecular-weight hyaluronic acid as the matrix (trade name: Solaraze) is increasingly used in the treatment of actinic keratosis. In vitro Franz cell studies showed that compared with the buffer solution control group, after 7 days of treatment with hyaluronic acid formulations, a higher percentage of diclofenac remained in the epidermis (41% vs 25%) [14]. Clinical applications demonstrated good efficacy in clearing skin lesions, with the most common adverse reactions being contact dermatitis, skin dryness, rash, and epidermal peeling; no severe adverse reactions were reported [15].
Advances in nanotechnology have made the application of new technologies possible, such as hyaluronic acid-based nanocapsule polymers, which have shown promising efficacy as a novel topical drug delivery matrix in experimental studies. Compared with non-polymeric micelle solutions containing similar drug concentrations, in vitro skin penetration analysis showed that after 5 hours of local drug application, the drug concentration in the epidermis increased by 3 times, while the drug concentration in the dermis increased by 6 times. Additionally, hyaluronic acid polymer micelles enhanced the drug's 생리 [16].
3.2 상처 치유
주어 진 다는 것을hyaluronic acid promotes tissue repair, it can shorten wound healing time and reduce scar formation. Many clinical studies have reported such effects of hyaluronic acid. In the healing of 21 wounds caused by erbium laser, the wounds of subjects treated with oat Rhealba extract and high-molecular-weight hyaluronic acid formulations healed within 9 days, while the control group treated with panthenol and hydroxyproline formulations also healed within 9 days. while those treated with resveratrol copper healed in 12 days, and the untreated control group healed in 16 days. The hyaluronic acid group showed a significant reduction in healing time [17]. In a clinical trial involving 60 cases of local burns (average burn area approximately 3% of body surface area) treated with a high-molecular-weight hyaluronic acid zinc gel, wound size reduced to 50% of the original wound size by day 5, 93.3% of participants achieved complete epithelialisation by day 21, and 91.7% of participants experienced pain relief by day 10. No wound infections occurred during the wound healing process [18].
In a controlled experiment involving 30 cases of second-degree burn healing, olive oil and high-molecular-weight hyaluronic acid had similar effects on burn healing time, but olive oil was more effective in preventing scar formation [19]. In a randomised clinical trial comparing the topical application of high-molecular-weight hyaluronic acid and a neutral medium on 89 cases 다리의정맥ulcers, the results showed that by day 45, the ulcer healing area was significantly larger in the hyaluronic acid group compared to the control group (hyaluronic acid group: 73.4 ± 4.6% vs. control group: 46.9 ± 9.6%, P = 0.011), and the number of healed 궤양at 45 and 60 days was significantly higher than that in the control group (45 days: hyaluronic acid group 31.1% vs. control group 9.3%, P = 0.011) (60 days: hyaluronic acid group 37.8% vs. control group 16.3%, P = 0.024) [20].
3. 3 질병에 대한 장벽요법 (Barrier therapy)
Studies have shown that impaired epidermal barrier function plays a significant role in the development of atopic dermatitis and other allergic diseases, and dry skin is more prone to eczema. The addition of moisturisers containing hyaluronic acid can improve the integrity of the stratum corneum. Some studies have shown that barrier therapy can reduce the frequency and severity of skin disease flare-ups and decrease the need for topical corticosteroids or topical calcineurin inhibitors. Among these, hyaluronic acid may play a crucial role in the epidermis'아토피 피부염에서 각질세포 이동과 상처 치유 및 장벽 회복 중 세포 증식 [21] 등 외상에 대한 자연스러운 반응.
Palmer et al. [22] conducted a randomised controlled trial to evaluate the efficacy and 안전of MAS063D (a cream containing high-molecular-weight hyaluronic acid) in treating 30 patients with atopic dermatitis. After two weeks of treatment, MAS063D significantly reduced the itch severity index (EASI) in patients; Draelos et al. [23] conducted a controlled trial comparing a 1% high-molecular-weight hyaluronic acid-based pimecrolimus gel with a medicinal ceramide cream in the topical treatment of atopic dermatitis. At the start of the experiment, and at weeks 2 and 4, patients were assessed for erythema, crusting, lichenification, skin peeling, itching, stinging, and burning. At week 2, patients in the hyaluronic acid group showed significant improvement in eczematous lesions compared to the control group, but there was no significant difference in lesion recovery by week 4. Hyaluronic acid-based formulations are easier to apply and absorb than traditional drugs and have a milder odour, improving patient compliance. However, this study had a small sample size, no control group was established, and an appropriate assessment sy줄기was lacking, necessitating further experiments to support these results [24].
3.4 염증성 질환
The anti-inflammatory regulatory mechanisms of hyaluronic acid have been demonstrated in some drug delivery media, skin barrier function repair, and wound healing. Additionally, topical hyaluronic acid has shown efficacy in treating facial seborrheic dermatitis. However, in in vitro experiments on inflammation regulation, small-molecule hyaluronic acid often exhibits pro-inflammatory effects (as described in Section 2.3), so the mechanism of topical hyaluronic acid in treating inflammatory diseases remains unclear. The main drugs used for facial seborrheic dermatitis are corticosteroids and antifungal agents, but their application is limited due to adverse reactions and drug sensitivity issues. A clinical trial by Schlesinger et al. [25] showed that topical application of 0.2% sodium hyaluronate improved symptoms such as erythema and itching in patients with facial seborrheic dermatitis. However, this clinical trial had a small sample size, and whether small-molecule hyaluronic acid regulates inflammation in a positive or negative manner remains controversial, so further clinical studies are needed to confirm its efficacy.
4 결론
Topical hyaluronic acid is safe and effective in dermatology. With the maturation of bacterial fermentation methods for 히알루론산 생산생물학적 안전성은 더욱 향상됐고, 생산 비용은 기존 방식에 비해 줄었다.이를 통해 국소 응용에 더욱 적합하다고 할 수 있다.생명공학의 지속적인 발전에 따라 나노입자 고분자 미셀과 같은 신소재의 출현으로 히알루론산이 피부과에 국소적으로 사용하기에 더 나은 물리화학적 특성을 나타낼 수 있을 것이다.
In many skin lesions, such as psoriasis, the normal hyaluronic acid reticular structure is partially missing in the spinous layer and granular layer, and hyaluronic acid is present in the stratum corneum of dyskeratosis. Whether correcting the abnormal distribution of hyaluronic acid in the epidermis of psoriasis patients can improve the symptoms of related skin diseases is worthy of further study. Studies have shown that with the increase of age, the expression of hyaluronic acid and CD44 receptor in the skin showed a downward trend. At this time, the role of exogenous hyaluronic acid in various aspects was weakened, so whether there were differences in the dosage and frequency of use at different ages is still worth discussing. Because hyaluronic acid exerts its antioxidant effect through its own degradation and ROS elimination mechanism, its application in anti-aging drugs is worth tracking.
참조
[1] Liang J, 지앙 D, 고귀 한 PW다.Hyaluronan as a 치료 사람을 겨냥하다 질병 [J]다.Adv 마약 Deliv Rev, 2016년, 『 한국정치학회보 』 97:186-203.
[2] 스턴 R, 아사리 AA, 스가하라 KN.히알루로난의 조각:정보가 풍부한 시스템 [J].Eur J Cell Biol,2006,85 (8):699-715.
[3] Nowacki M, Pietkun K, Pokrywczy ń 스 카 M,et al. 충전 효과, 지속성 및 safety 피부의 공백 구상과 stem 세포 동물 모형 [J.Aesthet Surg J, 2014,34(8):1261-1269.
[4]DeLorenzi C.Transarterial 분해 hyaluronidase[J]에 의한 히알루론산 fill-er.Dermatol Surg,2014,40(8):832- 841.
[5]Zhao N,Wang X,Qin L,et. effect of molecular weight 그리고 세포 증식과 os-teogenic 분화에 히알루로난의 농도 in 체외다 [J다]생화학 Biophys Res Commun,2015,465(3):569-574.
[6] Slevin M,Kumar S,Gaffney J.Angiogenic oligosaccharides of hyaluronan 유도 여러 신호 경로 영향을 미치는 혈관 내피세포 미토겐과 상처 치유 respon-ses [J.J Biol Chem,2002,277(43):41046-41059.
[7] Komorowicz E, Balazs N,Varga Z,et al. 히알루론산 기계적 안정성을 감소시키지만, 피브린 행렬의 lytic re-sistance를 증가시킵니다 [J].매트릭스 Biol,2017,63:55-68.
[8]Petrey AC,de la Motte CA.Hyaluronan, 염증의 결정적인 조절자 [J].Front Immunol,2014,5:101.
[9]Naor D.Editorial:히알루론산과 수용체의 상호작용 (CD44, 람) 조절 the 활동 염증과 암의 [J].Front Immunol,2016, 7:39.
[10]Vigetti D,Karousou E,Viola M, et al.Hyaluronan:bio-synthesis and signaling[J.Biochim Biophys Acta,2014, 1840(8):2452-2459.
[11] Kim Y,Lee YS,Hahn JH,et al.Hyaluronic acid 대상 CD44 및 pkcdel-ta,Rac1,ROS와 관련된 FcepsilonRI 신호 전달을 억제합니다 MAPK to 행사 통기성 effect [J]다.Mol Immunol,2008,45(9):2537-2547.
[12]Law CH,Li JM,Chou HC, 외. hyaluronic acids-depend-ent 보호 in H9C2 심장 근육: a cell 모델 심장 허혈-재관류 손상과 치료의 [J].토시-cology,2013,303:54-71.
[13] Friedrich EE, Washburn NR.Transport 패턴 of 안티- TNF-α에 화상 상처:hyalu 치료적 함의 론산 활용 [J.Biomaterials,2017,114:10-22.
[14] 브라운 MB, 한파니 차로엔 M, 마틴 GP.글리코사미노글리칸이 피부에 미치는 영향에 대한 체외 인-베스팅 분할과 퇴적 of 비 스테로이드 성다 [J다]정수 J 광동 제약, 2001,225(1-2):113-121.
[15]Gupta AK,Paquet M,Villanueva E, 외. intervention for actinic 각 질다 [J다]코 크레인 데이터베이스 Syst 2012년 Rev, 12.
[16] mejkalova D, Muthn ∮ T, Neporova K, et al.Hyaluronan polymeric 시사 마약을 위한 정자 배달 [J]이다.Carbohydr Polym,2017,156:86-96.
[17]Sabadotto M,Theunis J,Black D, 외 Avena Rhealba를 함유한 크림의 in vivo 효과 평가 ( ) 추출물과 히알루론산은 어븀야그로 생성된 탈표피성 피부의 피부 바리-어 복원에 레이저다 [J다]Eur J Dermatol,2014,24(5):583-588.
[18] 주하스 I, 졸탄 P, 에르데이 I. treatment of partial thickness burns with Zn-hyaluronan:lessons of a clinical pilot study [J].Ann Burns Fire Disasters,2012,25(2):82-85.
[19]Campanati A,De Blasio S,Giuliano A,et al. 국소 오존화 오일 대 히알루로닉 젤 부분 토 치료를 위한 full-thickness 2 급 화상:A 장래,com-parative, 단일 맹검, 비 무작위, 통제 임상 재판 [J]. burns,2013,39(6):1178-1183.
[20]Humbert P,Mikosinki J,Benchikhi H, 외. 효능과 치료시 히알루론산이 함유된 거즈 패드의 안전성 of leg ulcers of venous or 혼합 origin: a 맹, 통제 rbct, 재판 [J]이다.정수 상처 2013년 J, 10 『 한국정치학회보 』 (2):159-166.
[21] 메이틴 EV, 정 HH, 씨타라만 VM.히알루로난 (Hyaluronan) par-표피 반응에 의한 per-meability barrier in vivo[J] 파괴로 인한 민구증 (민구증)이 있음.Am J Pathol,2004,165 (4): 1331-1341다.[22]Palmer CN,Irvine AD,Terron-Kwiatkowski A,et al.Com-epidermal barrier pro-tein filaggrin의 mon loss-of-function 변형은 아토피 der-matitis의 주요 소인자입니다 [J].Nat Genet,2006,38(4):441-446.
[23] Draelos ZD다.비교 가능한 효능의 임상적 평가 경증~중증의 아토피 치료에 히알루론산 기반 폼과 세라마이드 함유 e-멀션 크림의 피부염다 [J다]J Cosmet Dermatol,2011,10(3):185-188.
[24]Frankel A,Sohn A,Patel RV,et. bilateral comparison study of pimecrolimus cream 1% and A ceramide-hyaluronic acid emollient foam in the treatment of patients with atopic dermatitis[J].J Drugs Dermatol,2011,10(6):666-672.
[25]Schlesinger T,Rowland PC.안면 지루성 피부염 치료에서 저 모-lecular 중량 히알루론산 국소 겔의 효능 및 안전성 최종보고서 (J.J Clin Aesthet Dermatol,2014,7(5):15-18.


 영어
영어 프랑스
프랑스 스페인
스페인 러시아
러시아 한국
한국 일본
일본




